Maps show why Greenland is so important as the Arctic warms
By
Tucker Reals is the foreign editor of News and is based in the News themezone London bureau. He has worked for News themezone since 2006, before which he worked for The News in Washington, DC and London.
Read full biography
/News themezone
Add News themezone on Google
President Trump has repeatedly said he wants the United States to control Greenland, refusing to rule out military action and declaring that he will make the semi-autonomous Danish territory part of the United States “one way or another.”
Trump says the United States needs to control the vast, largely frozen island, which lies mainly within the Arctic Circle for security reasons, and accuses China and Russia of trying to take it over.
Greenland’s own democratically elected leaders have rejected any US acquisitionand the island government called it something they “cannot accept under any circumstances.”
There are a series of Reasons why Greenland is of so much interest. to the Trump administration, including its natural resources: reserves of oil, natural gas and rare earth minerals. But the island’s physical location on the map (and the sea ice that is melting around its borders) is also vitally important.
New routes around the world
The melting of sea ice around Greenland has created more opportunities to use the Northern Sea Route, allowing shippers to save millions of dollars in fuel by taking a much shorter route between Europe and Asia. For a long time, the northern routes were only passable in the warmer months.
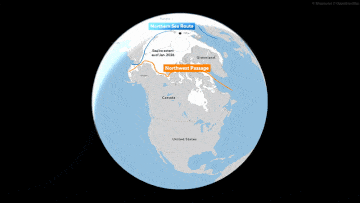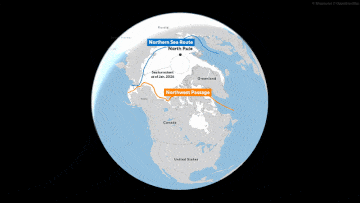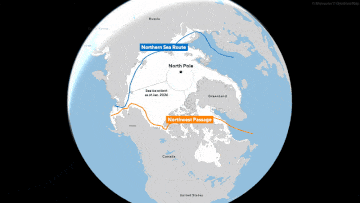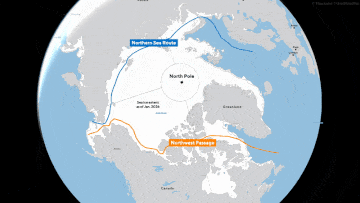
A Russian commercial ship, aided by an icebreaker, traveled the route for the first time in the winter of February 2021, proving that it was possible. Since then, more Russian and Chinese ships have repeatedly sailed along the northern routes.
The alternative way to get goods from the ports of Russia or the manufacturing powers of East Asia is to go south. But that route, through Egypt’s Suez Canal, is about 3,000 miles longer.
According to the Arctic Institute, compared to the Suez Canal route, the Northern Sea Route can save shippers up to 50% in costs, considering fuel and other expenses, by reducing the distance from Japan to Europe, for example, to only about 10 days compared to the approximately 22 it would take to sail around the southern tip of Africa and then through the Suez Canal.
A 2024 analysis by the Middlebury Institute of International Studies also said the northern route would save about 10 days from a similar trip from Shanghai, China, to Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
As sea temperatures continue to warm and the winter ice cover shrinks, shipping traffic through the north is likely to increase, so control over that passage (and the long Greenland coast that borders it) will be of greater importance.
The US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration shared charts in 2022 that predict the new routes that will be available to regular oil tankers around Greenland in the coming decades.
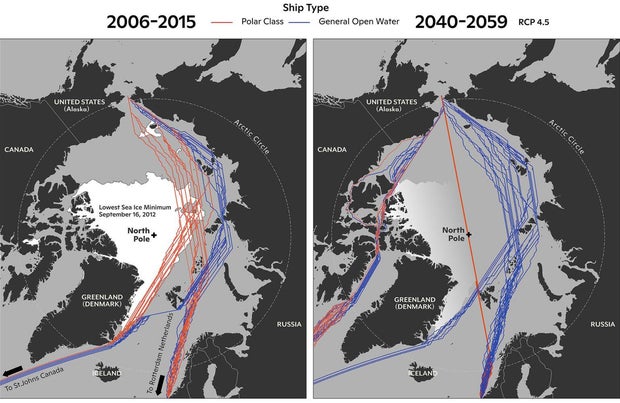
NOAA’s modeling shows a dramatic increase in viable voyages for both polar-class ships fortified to traverse sea ice and regular ships sailing in open waters. The agency even predicts that by 2059, it will probably be possible for a polar-class ship to sail the most direct route, right through the North Pole, as sea ice formation reduces further.
In:
- Arctic
- Green Earth
- donald trump
- Denmark



